HEARING CONDITIONS
Common Hearing Conditions

Age-Related Hearing Loss
Presbycusis involves degenerative changes to the inner ear. Typically, people who experience presbycusis don’t notice it until the significant loss has occurred because it tends to come on gradually and typically involves a hearing loss in both ears equally.

Tinnitus
Vast underlying pathophysiology but often the first and most common perception in adults and the geriatric population preceding the hearing loss. Gradual sensorineural hearing decline is often perceived as less urgent but patients seek tinnitus management more urgently.

Sudden Hearing Loss
Sudden sensorineural hearing loss has a significant chance to be reversed if acted upon by steroid regimen- if established within the first 3 days of onset and medication commenced.
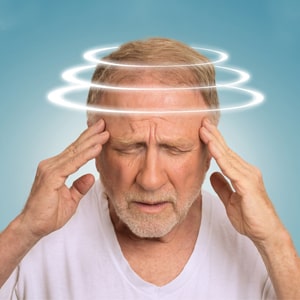
Vertigo
Most common underlying pathophysiology is peripheral (vestibular organ and vestibular nerve) e.g.: vestibular neuritis, BPPV, Meniere’s disease
Sensorineural Asymmetries
When hearing loss affects both ears to different degrees, this is called asymmetric hearing loss. Asymmetric hearing loss is diagnosed when one ear is significantly worse than the other in response to multiple frequencies.

Auditory Processing Disorders
Auditory processing disorder (APD) is a condition, generally affecting school-aged children where despite normal hearing, the kid can't understand what they hear in the same way other kids do.

Foreign Body Obstructions
It's not uncommon to experience the discomfort of having something caught in the ears. Most foreign objects get stuck in the ear canal, the narrow passageway that leads to the eardrum.

Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
Noise-induced hearing loss happens when the hair cells in the inner ear are overloaded and become damaged or die from too much noise. As the number of hair cells in the inner ear decreases, so does the ability to hear.
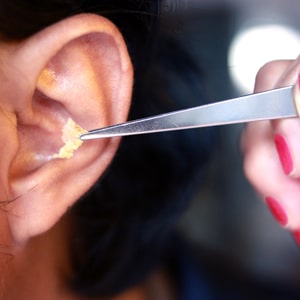
Earwax
Earwax is created by wax glands in the external ear canal, it protects the skin of the ear from water and infection. But when earwax builds up too much, it can cause a blockage within the ear, leading to a reduction in the ability to hear and possible damage to the eardrum.
Book an Appointment
Facing Hearing Issues?
If you are facing any trouble in hearing, book an appointment with our expert audiologist now.
Contact us
- 0493 493 485
